DYNATUNE DRIVE LINE & BRAKE SYSTEM DESIGN MODULES
DYNATUNE-XL does offers also "Longitudinal Dynamics Tools" which are in this ACCELERATING & BRAKING section explained. Two highly efficient tools have been developed for those people that need to modify their gear ratio's and get the best acceleration package with their available engine or want to improve/design the braking system and verify it's performance. The tools have recently been added to the product portfolio and are focused - as all DYNATUNE-XL tools - to deliver a maximum of information with a minimum of required input data.
Both tools are based on MS EXCEL ® workbooks and do only use standard workbook functions for all calculations (without any additional VBA code) and are therefore fully compatible with all Version of MS EXCEL ® from 2007 onwards.
Both tools are based on MS EXCEL ® workbooks and do only use standard workbook functions for all calculations (without any additional VBA code) and are therefore fully compatible with all Version of MS EXCEL ® from 2007 onwards.
DRIVE LINE DESIGN MODULE (DDM)
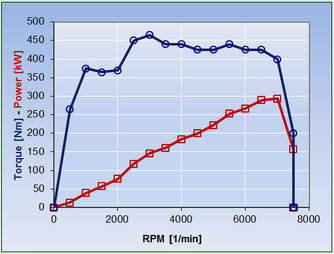
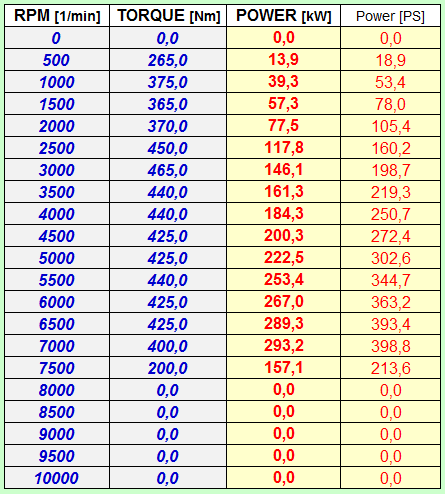
In the Drive Line Module most important data to be supplied are Engine Torque Map - either directly measured on an Engine Dyno or to be generated out of measured Power at the Wheel Data - as a function of RPM and Gearbox Ratios & Final Drive. The tool allows to calculate two vehicles and compare their key performance characteristics.
Drive line input data
|
The user can enter the Engine RPM / Torque Map of the engine with up to 21 data points allowing a precise reproduction of the engine data in steps of 500 RPM from 0 RPM up to 10.000 RPM - or in increments of 1000 RPM from 0 to 20.000 RPM - or in any other desired step size . |
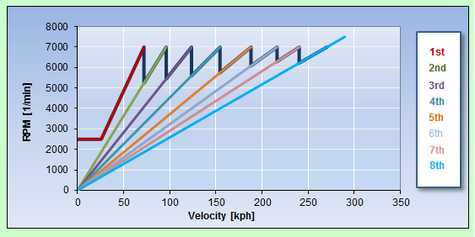
The Gearbox allows from 5 to up to 8 gear ratio's to be specified and can thus simulate the most commonly used (manual) gearboxes for automotive/motor cycle applications.
Shifting time can be entered in steps of 0.01 sec and the Power Train Architecture can be varied from FWD to AWD to RWD by 1 Parameter indicating the percentage of Torque transferred to the Rear Wheels. Together with the most important vehicle data, like Vehicle Mass, Weight Distribution, Aerodynamic Data and Tire Grip a typical Gear Ratio / Engine RPM - Velocity Chart provides at the blink of an eye the most important information about the Drive Line Layout.
|
|
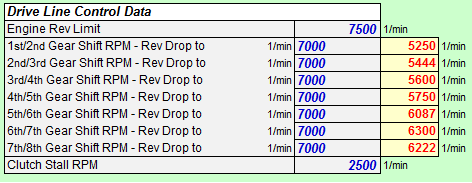
Drive Line Control Data can be entered. Next to the already mentioned Shift Time for each Gear an Up-Shift RPM can be set and the rev limit of the Engine. RPM drops are automatically calculated providing the numerical data for the Engine/Gearbox RPM Velocity chart.
Additionally the clutch Stall RPM parameter allows to investigate and find the optimal engine speed for Performance Starts. |
VEHICLE Data
|
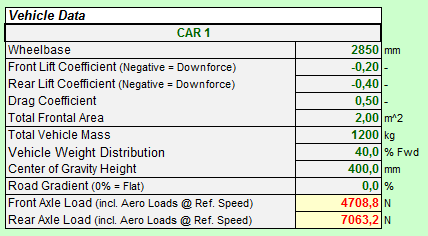
The most important vehicle data are of course Vehicle Mass, Weight Distribution, Center of Gravity Height and Wheelbase since these parameters define the longitudinal load transfer and wheel loads under Acceleration. Additionally the tool considers the Aerodynamic Data, Tire Rolling Resistance and Road Gradient (included for Hill Climb Racing), since these are the limiting parameters of any Acceleration.
It should be mentioned that the tool is fully capable of simulating high down force vehicles and considers the effects of especially high (negative) Lift & Drag Coefficients on acceleration performance. The axle loads can be generated for any desired speed, if wanted |
RESULTS
|
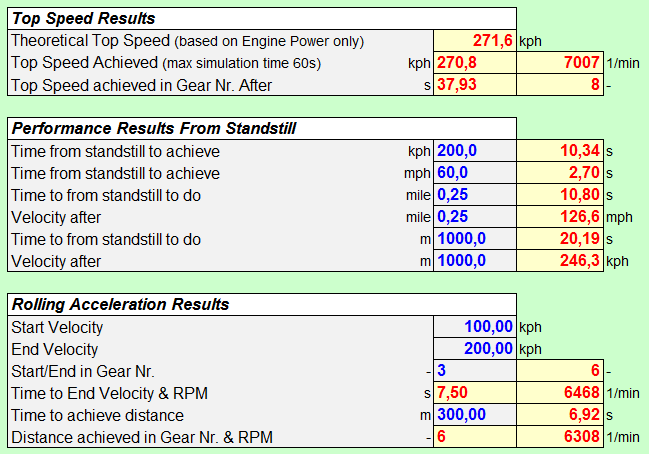
NUMERICAL RESULTS contain the most commonly known numbers that are being used in Performance Tests either related to Time or Distance. All points of interest can be varied without any limits as long as the maximum (simulation) time which is needed to achieve this condition does not exceed 1 minute.
As a guidance the tool calculates automatically the theoretical maximum speed that should be achievable - solely based on the amount of Power available - which will help to identify any potential issues on the selected gear ratio's or final drive. The tool will also automatically calculate the maximum possible accelerations for FWD or RWD and the best AWD configuration (with corresponding Front to Rear Torque Distribution) in order to achieve maximum acceleration at a given speed. |
GRAPHICAL RESULTS consist out of various Graphs. Next to several Time History Plot's there are two important "major" Graphs:
In the first Graph is the maximum Acceleration of the vehicle is plotted versus it's Velocity for each available Gear considering the limits of Tire Grip and the combined effects of Rolling Resistance, Aerodynamic Resistance & Road Gradient (which is for instance quite important for Hill Climbers). The second Graph plots the sum of all of these limiting factors into the Engine Torque Map allowing the user to see immediately whether the selection of ratio's is optimal or not.
In the first Graph is the maximum Acceleration of the vehicle is plotted versus it's Velocity for each available Gear considering the limits of Tire Grip and the combined effects of Rolling Resistance, Aerodynamic Resistance & Road Gradient (which is for instance quite important for Hill Climbers). The second Graph plots the sum of all of these limiting factors into the Engine Torque Map allowing the user to see immediately whether the selection of ratio's is optimal or not.
The remaining 6 other plots provide all visual information needed to complete the analysis of Vehicle Acceleration, Velocity and Distance. Since Acceleration vs. Velocity is a key metric, this information can directly be confronted with the Saturation of the Tire Grip, allowing to identify when wheel spin occurs (or stops) and what stall clutch RPM would give optimal traction in 1st Gear.
The workbook contains also a COMPARISON Sheet in which all key Parameters and Graphs for 2 Vehicles are listed allowing an easy back to back comparison of variants. Have a look at the DDM PDF file to find out more about it.
BRAKE SYSTEM DESIGN MODULE (BDM)
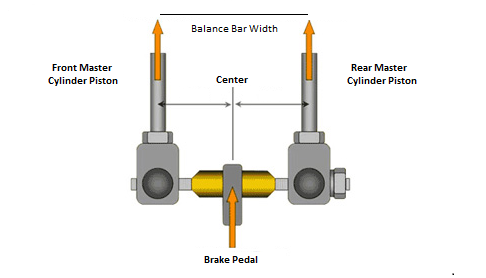
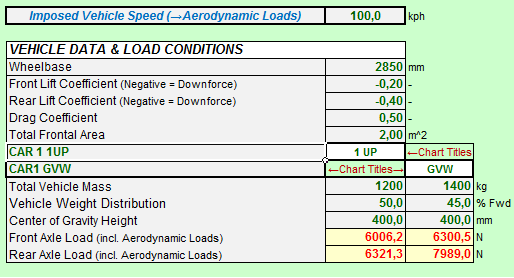
In the Brake System Module the most important data to be supplied are Brake Disc Dimensions, Caliper Piston Diameters and Master Cylinder / Brake Pedal Data . The tool allows to investigate two vehicles in two load conditions and compare their key performance characteristics. The Tool is designed for Caliper/Disc Systems, does NOT consider any Brake Boost Devices and is governed by a Brake Balance Bias Bar which defines the Brake Distribution between the Front and Rear Axle.
BRAKE SYSTEM input data
|
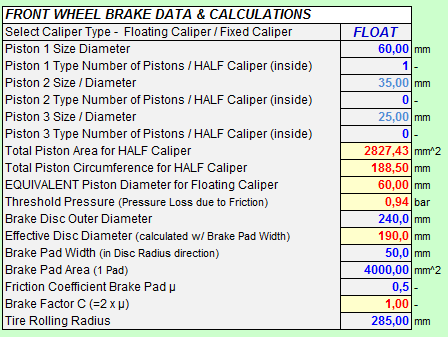
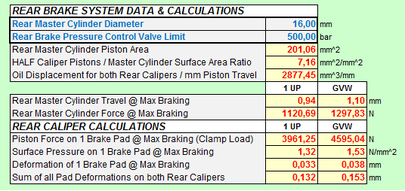
As to be expected, the main Brake System Data to be supplied are those of the Brake Calipers and Discs. The calculation algorithm is based on the principle of a 1 Piston Floating Caliper (piston located at the inside of the disc) and will convert all data of Fixed (multi-piston) Calipers to that principle. Up to 3 different sizes of pistons can be used allowing maximum flexibility in geometric design.
Next to the data for Front & Rear Wheel Brakes, the Master Cylinders Dimensions have to be provided and some basic geometry data of the Brake Balance Bias Bar. |
And some Specific Data to consider the effects of Piston Friction and Brake Pad Deformation.
|
VEHICLE Data
|
The most important vehicle data are of course Vehicle Mass, Weight Distribution, Center of Gravity Height and Wheelbase since these parameters define the longitudinal load transfer and wheel loads under Braking. Additionally the tool can consider two load conditions of the vehicle.
It should be mentioned that the tool is fully capable of simulating high down force vehicles and considers the effects of especially high (negative) Lift & Drag Coefficients on Braking Performance. The axle loads are generated for the imposed speed. |
RESULTS
|
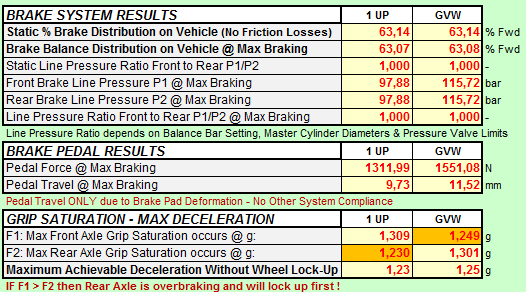
NUMERICAL RESULTS show the most interesting metrics of the Braking System for 2 Load Conditions. Key Brake Operating Characteristics are Brake Line Pressure (& Ratio Front to Rear) and Brake Pedal Force % Travel. Based on the provided Vehicle & Tire Data the tool calculates automatically the Grip Saturation at each Axle for the given Brake Balance Distribution
Beyond that all interesting details of the Braking System are available as intermediate results. A Brake Pressure Control Valve can limit the maximum Brake Line Pressure if needed. |
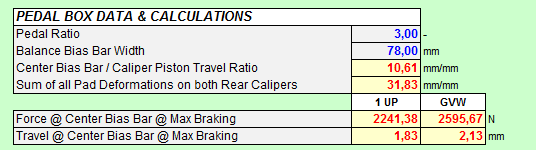
And also all important details of the Brake Pedal
|
And the final Vehicle Result: Stopping Distance
GRAPHICAL RESULTS consist out of 3 Graphs from which the classical Axle Grip Saturation vs. Vehicle Deceleration Graph is the most important. The other Graphs show Brake System Actuation Forces and Displacements..All Graphs contain an indication of the Physical Limit of the Vehicle. Beyond that, some of the EU-Homologation requirements are considered in the first graph as a reference guide for street legal vehicles.
This workbook contains also a COMPARISON Sheet in which all key Parameters and Graphs for 2 Vehicles (and their 2 load conditions) are listed allowing an easy back to back comparison of variants. Have a look at the BDM PDF file to find out more about it.